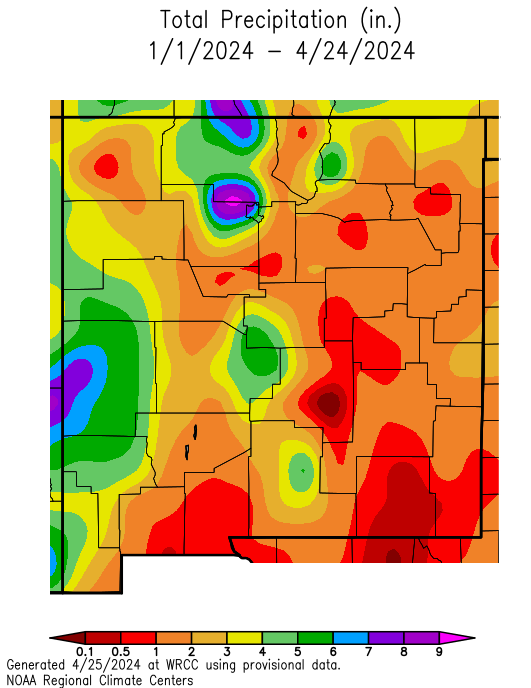
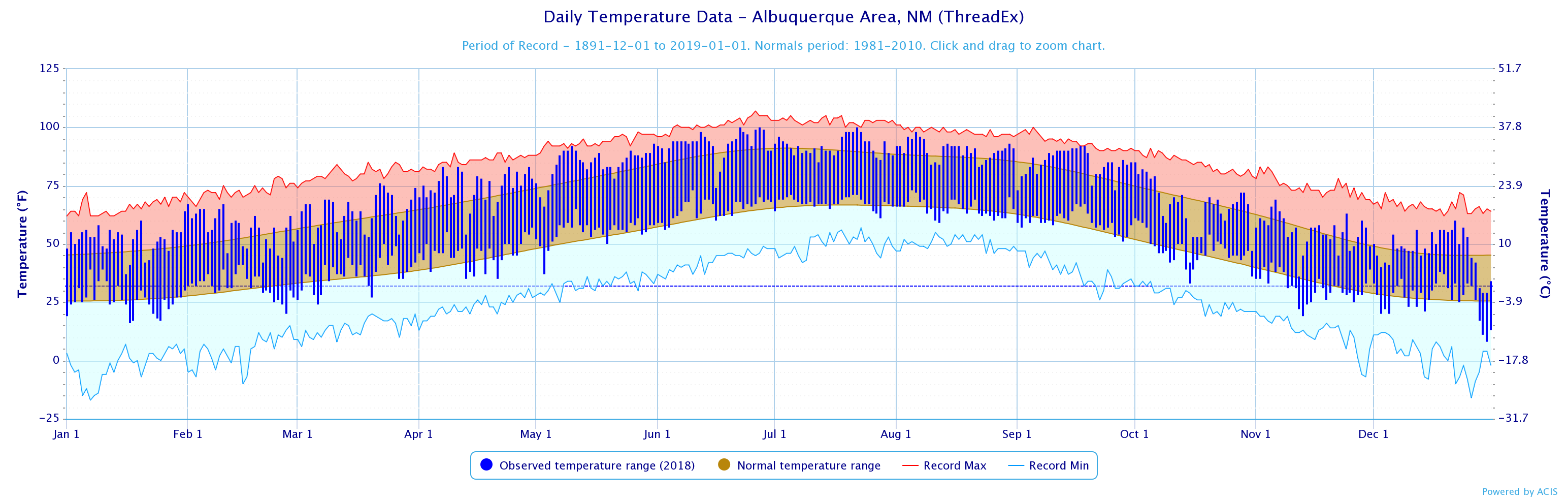
Albuquerque, often affectionately referred to as ABQ, experiences distinct rainfall patterns shaped by its geography and climate. Grasping these patterns is vital for residents, farmers, and businesses to effectively prepare for seasonal changes. Whether you're planning a trip or managing water resources, this guide will provide in-depth insights into ABQ's rainfall trends and their implications.
Rainfall plays a pivotal role in shaping the ecosystem and daily life in Albuquerque. As one of the fastest-growing cities in the Southwest, understanding ABQ's rainfall isn't merely about tracking weather patterns—it's about ensuring sustainable living and resource management. This article will delve into the nuances of ABQ's rainfall, including its seasonal variations, historical data, and the environmental and societal impacts.
In the following sections, we will explore everything you need to know about ABQ's rainfall. From the geographical factors influencing precipitation to practical strategies for preparing for wet seasons, this guide aims to offer actionable insights for both residents and visitors. Let’s begin!
Read also:Kohls Sheboygan Wisconsin Your Ultimate Shopping Destination
Table of Contents
- Overview of ABQ Rainfall
- Geographical Influences on ABQ Rainfall
- Seasonal Variations in ABQ Rainfall
- Historical Insights and Trends
- Climate Change and Its Impact on ABQ Rainfall
- The Monsoon Season in Albuquerque
- Techniques for Measuring Rainfall
- Preparing for Wet Seasons
- Environmental Implications of ABQ Rainfall
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Overview of ABQ Rainfall
Located in the heart of New Mexico, Albuquerque boasts a semi-arid climate that significantly influences its rainfall patterns. ABQ's rainfall is characterized by distinct seasonal variations, with the majority of precipitation occurring during the summer monsoon season. Understanding these patterns is crucial for residents, as it affects everything from agriculture to urban planning and beyond.
On average, Albuquerque receives approximately 9 inches of rainfall annually, which is relatively low compared to other regions in the United States. However, the distribution of this rainfall is uneven, with significant year-to-year fluctuations. This variability underscores the importance of staying informed about weather forecasts and long-term climate trends for effective planning and resource management.
In this section, we will explore the basics of ABQ rainfall, including its role in sustaining local ecosystems and the challenges posed by its inconsistency. By understanding these fundamentals, we can better appreciate the significance of rainfall in Albuquerque's unique climate.
Geographical Influences on ABQ Rainfall
Topography and Elevation
The geographical features of Albuquerque play a critical role in determining its rainfall patterns. Situated at an elevation of approximately 5,300 feet above sea level, the city's topography influences how air masses move across the region. The Sandia Mountains to the east and the Rio Grande Valley to the west create a unique microclimate that directly impacts precipitation levels.
Proximity to Desert Landscapes
Albuquerque's location in the southwestern United States, surrounded by desert landscapes, contributes to its semi-arid climate. The nearby Chihuahuan Desert and Colorado Plateau significantly influence the amount and frequency of rainfall in the area. These deserts act as barriers to moisture-laden air masses, resulting in lower overall precipitation levels.
Understanding these geographical factors is essential for predicting rainfall patterns and preparing for potential droughts or floods. By analyzing the interplay between topography, elevation, and surrounding landscapes, meteorologists can provide more accurate forecasts for ABQ rainfall, helping residents and businesses plan accordingly.
Read also:Unleashing The Power Of Shelby Rush Energy Your Ultimate Guide
Seasonal Variations in ABQ Rainfall
ABQ rainfall exhibits distinct seasonal variations, with the majority of precipitation occurring during the summer months. This pattern is primarily driven by the North American Monsoon system, which brings moisture from the Gulf of Mexico and the Pacific Ocean to the southwestern United States.
Summer Monsoon Season
- June through September marks the peak monsoon season in Albuquerque.
- During this period, thunderstorms are frequent, providing much-needed rainfall to the region.
- Approximately 40% of Albuquerque's annual rainfall occurs during the monsoon season, making it a critical period for replenishing water resources.
Winter Rainfall
In contrast, winter rainfall in Albuquerque is relatively sparse. Cold air masses from the north often result in dry conditions, with occasional snowfall in the higher elevations. However, winter precipitation is crucial for replenishing groundwater supplies and supporting vegetation during the dry spring months, making it an essential component of the region's hydrological cycle.
Historical Insights and Trends
Historical data on ABQ rainfall provides valuable insights into long-term trends and patterns. According to records from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Albuquerque has experienced fluctuations in annual rainfall over the past century.
- Average annual rainfall in Albuquerque has remained relatively stable at around 9 inches.
- However, there have been notable variations, with some years experiencing significantly higher or lower precipitation levels.
- For instance, the city recorded its highest annual rainfall in 1941 at 17.4 inches and its lowest in 1956 at 3.6 inches, highlighting the variability in precipitation over time.
These historical records emphasize the importance of understanding rainfall variability and its potential impacts on local ecosystems and water resources, helping stakeholders make informed decisions about resource management and planning.
Climate Change and Its Impact on ABQ Rainfall
Climate change is increasingly affecting rainfall patterns worldwide, and Albuquerque is no exception. Rising global temperatures are altering the frequency and intensity of precipitation events, leading to more extreme weather conditions.
Potential Effects on ABQ Rainfall
- Increased variability in rainfall, with more intense storms and prolonged dry periods, poses challenges for water resource management.
- Potential shifts in the timing of the monsoon season could disrupt agricultural practices and water management strategies, requiring adaptive measures.
- Higher evaporation rates due to warmer temperatures may exacerbate drought conditions, further straining water resources.
Addressing these challenges requires proactive measures, such as improving water conservation practices and investing in climate-resilient infrastructure. By adapting to changing rainfall patterns, Albuquerque can ensure sustainable development and resource management for future generations.
The Monsoon Season in Albuquerque
The monsoon season is a defining feature of ABQ rainfall, bringing much-needed moisture to the arid landscape. This period, typically lasting from June to September, is characterized by frequent thunderstorms and heavy rainfall, playing a crucial role in the region's hydrological cycle.
Causes of the Monsoon
The North American Monsoon system is responsible for the increased rainfall during this time. As warm air rises over the desert regions, it creates a low-pressure zone that draws in moist air from the Gulf of Mexico and the Pacific Ocean. This moisture-laden air condenses into clouds, resulting in thunderstorms and heavy rainfall that rejuvenate the landscape.
Benefits and Challenges
- Monsoon rains help replenish water supplies and support vegetation growth, providing essential resources for local ecosystems.
- However, they can also cause flash flooding and damage to infrastructure, posing risks to both property and human safety.
Understanding the dynamics of the monsoon season is crucial for mitigating its negative impacts while maximizing its benefits, ensuring a balanced approach to water resource management and environmental protection.
Techniques for Measuring Rainfall
Accurate measurement of ABQ rainfall is essential for monitoring climate trends and managing water resources. Meteorologists use various techniques to collect and analyze precipitation data, ensuring reliable and actionable information for stakeholders.
Rain Gauges
Rain gauges remain the most common method for measuring rainfall. These devices collect rainwater in a calibrated container, allowing scientists to determine the amount of precipitation that has fallen over a specific period. Their simplicity and reliability make them indispensable tools for meteorological research.
Satellite Imagery
Modern technology, such as satellite imagery, provides valuable insights into rainfall patterns across large areas. Satellites can detect precipitation from space, offering a broader perspective on weather systems affecting Albuquerque and its surrounding regions. By combining traditional and advanced measurement techniques, meteorologists can provide more accurate forecasts and long-term climate assessments.
Preparing for Wet Seasons
Residents of Albuquerque can take several proactive steps to prepare for wet seasons and mitigate potential risks associated with heavy rainfall. Effective planning and preparation are essential for safeguarding homes, communities, and infrastructure during periods of increased precipitation.
Homeowners' Tips
- Ensure proper drainage systems are in place to prevent flooding and water damage to properties.
- Install rain barrels to collect and reuse rainwater for gardening and other non-potable purposes, promoting water conservation.
- Regularly inspect roofs and gutters for damage or blockages to ensure they function effectively during heavy rainfall events.
Community Initiatives
Local governments and organizations can promote community initiatives to enhance flood preparedness and water conservation efforts. By fostering collaboration and shared responsibility, residents can create a more resilient and sustainable environment for all, minimizing the impacts of extreme weather events.
Environmental Implications of ABQ Rainfall
ABQ rainfall has significant environmental implications, both positive and negative. Understanding these effects is crucial for maintaining ecological balance and promoting sustainable development in the region.
Positive Impacts
- Rainfall supports local vegetation and wildlife, maintaining biodiversity in the region and preserving its unique ecosystems.
- It helps recharge groundwater supplies, ensuring a stable water source for future use and supporting agricultural and urban needs.
Negative Impacts
- Heavy rainfall can lead to soil erosion and habitat destruction, disrupting natural landscapes and threatening local flora and fauna.
- Flash floods pose significant risks to infrastructure and human safety, highlighting the need for adaptive management strategies and emergency preparedness.
By addressing these challenges through conservation efforts and adaptive management strategies, Albuquerque can preserve its natural resources and protect its ecosystems for generations to come.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, understanding ABQ rainfall is essential for residents, businesses, and policymakers in Albuquerque. From the geographical factors influencing precipitation to the impacts of climate change, this guide has provided comprehensive insights into the city's rainfall patterns and their implications for sustainable living and resource management.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with ABQ rainfall in the comments below. Your feedback helps us improve our content and provide valuable information to the community. Additionally, explore other articles on our site for more insights into climate and weather patterns in the Southwest, empowering you to make informed decisions and contribute to a sustainable future.