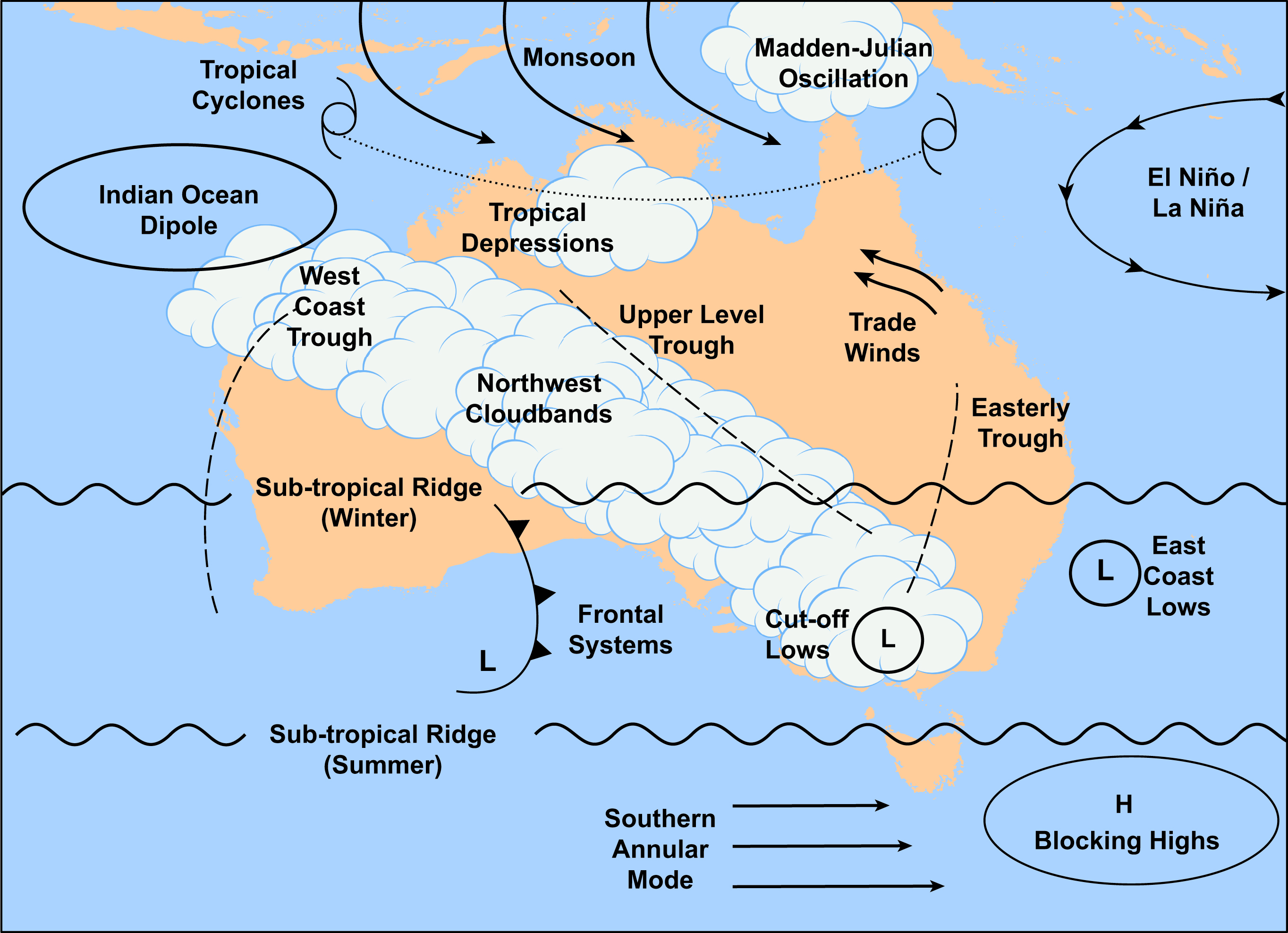
Western Australia (WA) boasts a remarkable variety of climates, ranging from tropical conditions in the north to temperate climates in the south. Gaining a thorough understanding of WA's climate is crucial for residents, tourists, and businesses, as it directly influences daily life, agricultural practices, and tourism. Whether you're planning a visit or contemplating a move, this guide delves into the intricate climate patterns of WA.
Spanning a vast expanse, Western Australia features highly variable climatic conditions across its numerous regions. From the monsoon-driven rains of the Kimberley to the Mediterranean climate of Perth, each area exhibits distinct weather traits that define its environment and way of life. This article will meticulously examine these variations, equipping you with valuable insights to inform your decisions regarding WA.
As we investigate WA's climate, it's vital to acknowledge the impact of global climate change on regional weather patterns. Increasing temperatures and evolving rainfall trends are reshaping traditional climate norms, presenting new challenges for the state's ecosystems and communities. This guide seeks to offer practical knowledge to help you effectively navigate these changes.
Read also:Exploring The Beauty And Bounty Of Stream Cliff Farms
Insights into Western Australia's Climate
Overview of Western Australia's Climate Zones
Western Australia is segmented into several distinct climate zones, each shaped by its geographical positioning, proximity to the ocean, and elevation. The northern regions are characterized by tropical climates marked by wet and dry seasons, whereas the southern areas display a more temperate, Mediterranean-like climate.
The central desert regions, encompassing the Great Sandy Desert and Gibson Desert, are distinguished by arid conditions with significant temperature variations between day and night. These zones receive minimal rainfall, making water conservation a critical issue for local communities. Understanding these zones is essential for planning sustainable development in the region.
Seasonal Dynamics in WA
The climate of WA follows well-defined seasonal patterns that differ across regions. In the north, the wet season spans from November to April, bringing heavy rainfall and occasional cyclones. The dry season, from May to October, provides warm, sunny weather, perfect for outdoor adventures.
Conversely, the southern regions experience four distinct seasons. Summers are generally hot and dry, while winters bring mild temperatures and occasional rainfall. This seasonal diversity supports a rich array of flora and fauna, establishing WA as a biodiversity hotspot. Understanding these seasonal patterns is key to planning activities and travel in the state.
Regional Climate Breakdown
Kimberley Region
The Kimberley region in northern WA is celebrated for its tropical climate. During the wet season, heavy monsoonal rains dramatically transform the landscape, creating breathtaking waterfalls and lush vegetation. The dry season features pleasant temperatures ranging from 25°C to 35°C, making it an ideal time to explore the region's natural attractions.
- Wet season: November to April
- Dry season: May to October
- Average rainfall: 600-1,500 mm annually
- Temperature range: 25°C to 40°C
Pilbara Region
The Pilbara region experiences a semi-arid climate with hot summers and mild winters. Known for its extreme temperature fluctuations, daytime temperatures often surpass 40°C during summer. Despite its arid conditions, the Pilbara sustains unique ecosystems adapted to the harsh environment, offering a fascinating study in ecological resilience.
Read also:Exploring The Vibrant Charm Of The City Of North Mankato
- Summer temperatures: 35°C to 50°C
- Winter temperatures: 10°C to 25°C
- Average rainfall: 200-300 mm annually
Perth's Mediterranean Climate
Weather Patterns in Perth
Perth, the capital city of WA, enjoys a Mediterranean climate characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters. This climate fosters a thriving wine industry and supports an active outdoor lifestyle. Residents and visitors can anticipate clear skies during summer and occasional rain showers in winter.
Data from the Bureau of Meteorology indicates that Perth's average annual rainfall has been steadily declining over the past few decades, raising concerns about water security and urban planning. In response, the city's government has introduced various initiatives, including water recycling programs and sustainable development projects, to address these challenges.
Climate Change and Its Impact on WA
Rising Temperatures
Global climate change is profoundly affecting WA's weather patterns. Rising temperatures have resulted in more frequent heatwaves, particularly in the southern regions. Over the past few decades, the number of days exceeding 35°C has significantly increased, impacting agriculture, health, and infrastructure.
A study published in the Journal of Climate reveals that WA's average temperature has risen by 1°C since the early 20th century. Projections suggest a potential increase of 2-4°C by the end of the century, underscoring the urgency of addressing these changes.
Changing Rainfall Patterns
WA's rainfall patterns are undergoing significant alterations. The southwestern part of the state has witnessed a 15-20% reduction in winter rainfall over the past 50 years, posing challenges for agriculture, water supply, and ecosystem health.
Scientists attribute these changes to shifting weather systems caused by global warming. As the planet warms, the subtropical high-pressure systems influencing WA's weather are moving further south, diminishing the frequency of cold fronts that deliver rain to the region.
Strategies for Adapting to WA's Climate
Water Management Innovations
In response to the challenges posed by changing climate conditions, WA has adopted various water management strategies. These include desalination plants, groundwater replenishment programs, and water efficiency initiatives. For instance, the Perth Seawater Desalination Plant supplies approximately 40% of the city's drinking water, ensuring a reliable water source regardless of rainfall.
- Desalination plants: Provide consistent water supply irrespective of rainfall
- Groundwater replenishment: Recharge aquifers using treated wastewater
- Water efficiency programs: Promote conservation through incentives and education
Sustainable Agriculture Practices
Farmers in WA are adapting to evolving climate conditions by embracing sustainable agriculture practices. These include crop diversification, soil conservation techniques, and precision irrigation systems. The Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development offers resources and support to assist farmers in implementing these strategies effectively.
Research conducted by the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) emphasizes the importance of climate-smart agriculture in ensuring food security and environmental sustainability. By adopting innovative practices, WA's agricultural sector can continue to thrive despite the challenges posed by climate change.
Climate and Tourism in WA
Seasonal Tourism Opportunities
WA's diverse climate offers a multitude of tourism opportunities throughout the year. During the dry season in the north, visitors can explore the awe-inspiring landscapes of the Kimberley and Pilbara regions. In the south, Perth's Mediterranean climate and its surroundings provide an ideal setting for outdoor activities and cultural experiences.
- Kimberley: Best visited during the dry season (May to October)
- Pilbara: Perfect for adventure tourism year-round
- Perth: Offers pleasant weather and events all year
Climate Considerations for Travelers
When planning a trip to WA, it's essential to consider the regional climate and seasonal variations. Travelers should pack suitable clothing and gear for the specific areas they intend to visit. For example, lightweight clothing and sun protection are crucial for northern regions, while warmer layers may be necessary for southern areas during winter.
Moreover, visitors should be aware of potential weather hazards, such as cyclones in the north and bushfires in the south. Staying informed about weather conditions and adhering to safety guidelines can ensure a safe and enjoyable experience in WA.
Scientific Research on WA's Climate
Key Studies and Findings
Several scientific studies have explored WA's climate and its future projections. A report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) highlights the increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events in the region, including heatwaves, droughts, and heavy rainfall.
Local research conducted by the University of Western Australia and CSIRO provides valuable insights into the impacts of climate change on WA's ecosystems and communities. Their findings underscore the necessity of adaptive strategies and collaborative efforts to mitigate these effects.
Data and Statistics
According to the Bureau of Meteorology, WA's climate trends reveal the following key statistics:
- Average temperature increase: 1°C since the early 20th century
- Winter rainfall decline: 15-20% in southwestern WA over the past 50 years
- Sea level rise: Approximately 8 mm per year along WA's coastline
These figures emphasize the urgency of addressing climate change impacts in WA and implementing effective adaptation measures.
Community and Government Initiatives
Local Climate Action Plans
Various local governments in WA have developed climate action plans to tackle the impacts of climate change. These plans focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions, enhancing community resilience, and promoting sustainable development. For instance, the City of Perth aims to achieve carbon neutrality by 2025 through renewable energy projects and energy efficiency programs.
Community engagement is pivotal to the success of these initiatives. By involving residents, businesses, and stakeholders in decision-making processes, local governments can create more effective and inclusive climate solutions.
Statewide Policies and Programs
The Western Australian government has enacted several policies and programs to address climate change challenges. These include the Climate Change Response Strategy, which outlines a comprehensive approach to reducing emissions and enhancing adaptation capabilities.
Additionally, the government provides funding and support for renewable energy projects, energy efficiency improvements, and sustainable transport initiatives. By investing in these areas, WA aims to transition to a low-carbon economy while ensuring economic growth and social well-being.
Conclusion
In summary, the climate of WA is a complex and dynamic system that significantly influences the state's environment, economy, and lifestyle. From the tropical conditions of the north to the Mediterranean climate of Perth, each region presents unique opportunities and challenges. Understanding these variations and adapting to changing climate conditions is essential for ensuring a sustainable future for WA.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences about WA's climate in the comments below. Your insights can help others better understand this captivating region. Furthermore, we invite you to explore our other articles on environmental topics and stay informed about the latest developments in climate science.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Climate of WA
- Regional Climate Analysis
- Perth's Mediterranean Climate
- Impact of Climate Change on WA
- Adaptation Strategies for WA's Climate
- Climate and Tourism in WA
- Scientific Research on WA's Climate
- Community and Government Initiatives
- Conclusion