The Pouch of Douglas, also known as the rectouterine pouch or rectovaginal pouch, is a fascinating anatomical structure that plays a crucial role in human physiology. This area, located at the posterior cul-de-sac of the peritoneal cavity, is essential for diagnosing various medical conditions and understanding the female reproductive system. If you're looking to dive deeper into its importance and functions, this article will provide you with everything you need to know.
Understanding the anatomy and physiology of the human body is essential for healthcare professionals and individuals alike. The Pouch of Douglas, in particular, holds significant importance due to its role in diagnosing and treating various medical conditions. This article will explore its structure, functions, and clinical relevance.
By the end of this article, you'll have a clearer understanding of what the Pouch of Douglas is, its importance in medical diagnostics, and how it relates to the overall health of the female reproductive system. Let's begin by exploring its anatomical details and functions.
Read also:Jimmy Fallon Birthday Celebrating The Life And Career Of A Latenight Legend
Table of Contents
- Anatomy of the Pouch of Douglas
- Functions of the Pouch of Douglas
- Role in Diagnosis
- Common Medical Conditions
- Treatment Options
- Preventive Measures
- Historical Background
- Current Research
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Anatomy of the Pouch of Douglas
The Pouch of Douglas is a recess in the peritoneal cavity, situated between the rectum and the posterior wall of the uterus in females. It is the deepest point of the peritoneal cavity and is named after James Douglas, the Scottish anatomist who first described it. This anatomical structure is crucial for understanding various gynecological and abdominal conditions.
Location and Structure
Located in the pelvis, the Pouch of Douglas is bordered by the rectum posteriorly and the uterine fundus anteriorly. It is a potential space that can accumulate fluid, making it a key area for diagnosing conditions such as endometriosis or pelvic inflammatory disease.
Key anatomical features include:
- Peritoneal lining
- Rectal wall
- Uterine wall
- Pelvic floor muscles
Functions of the Pouch of Douglas
The Pouch of Douglas serves several important functions in the human body. Its primary role is to facilitate the movement of fluid within the peritoneal cavity, allowing for the distribution of nutrients and the removal of waste products.
Physiological Role
One of the critical functions of the Pouch of Douglas is its involvement in the immune response. The fluid collected in this area can contain immune cells that help fight infections and prevent the spread of pathogens within the abdominal cavity.
Role in Diagnosis
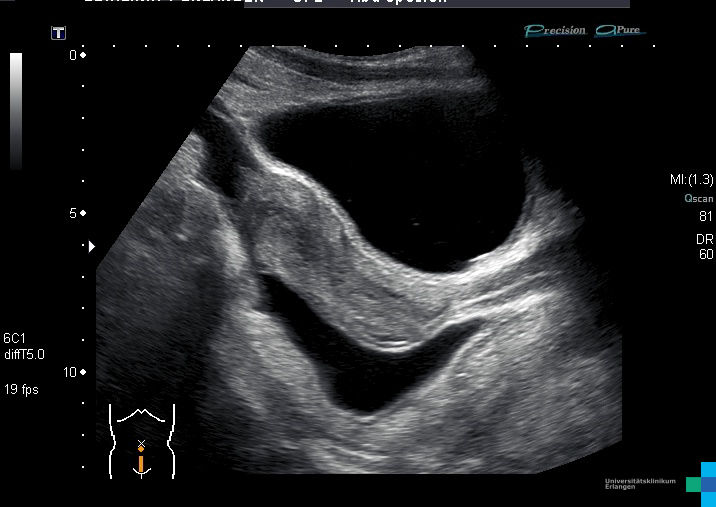
The Pouch of Douglas plays a vital role in diagnosing various medical conditions, particularly those affecting the female reproductive system. Healthcare professionals often use imaging techniques and physical examinations to assess this area for abnormalities.
Read also:Discover The Vibrant Spirit Of Temple Shir Tikva Wayland A Community Of Faith And Connection
Diagnostic Techniques
Common diagnostic methods include:
- Transvaginal ultrasound
- MRI
- Laparoscopy
These techniques allow for a detailed examination of the Pouch of Douglas, helping to identify conditions such as endometriosis, ovarian cysts, and pelvic infections.
Common Medical Conditions
Several medical conditions are associated with the Pouch of Douglas. Understanding these conditions is essential for effective diagnosis and treatment.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterine cavity, often affecting the Pouch of Douglas. Symptoms may include pelvic pain, infertility, and painful menstruation.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
PID is an infection of the female reproductive organs that can lead to the accumulation of pus in the Pouch of Douglas. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications.
Treatment Options
Treatment for conditions affecting the Pouch of Douglas varies depending on the underlying cause. Surgical intervention, medication, and lifestyle changes are common approaches.
Surgical Procedures
In cases where surgery is necessary, procedures such as laparoscopy or laparotomy may be performed to remove abnormal tissue or drain accumulated fluid.
Preventive Measures
Preventing conditions associated with the Pouch of Douglas involves maintaining good reproductive health and seeking early medical attention for symptoms.
Tips for prevention include:
- Regular gynecological check-ups
- Practicing safe sex
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle
Historical Background
The Pouch of Douglas was first described by James Douglas in the early 18th century. His detailed anatomical studies laid the foundation for modern understanding of this structure. Over the years, advancements in medical technology have enhanced our ability to diagnose and treat conditions related to this area.
Current Research
Ongoing research focuses on improving diagnostic techniques and treatment options for conditions affecting the Pouch of Douglas. Studies are exploring the use of advanced imaging technologies and minimally invasive surgical procedures to enhance patient outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Causes Fluid Accumulation in the Pouch of Douglas?
Fluid accumulation can result from conditions such as endometriosis, infections, or malignancies. Prompt medical evaluation is essential to determine the underlying cause.
How is the Pouch of Douglas Examined During Diagnosis?
Examination typically involves imaging techniques like ultrasound or MRI, along with physical examinations and laboratory tests.
Conclusion
The Pouch of Douglas is a vital anatomical structure with significant clinical relevance. Understanding its anatomy, functions, and associated conditions is crucial for maintaining reproductive health. By staying informed and seeking timely medical care, individuals can effectively manage and prevent complications related to this area.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from this information. For more insights into health-related topics, explore our other articles and resources. Your feedback and questions are always welcome!