When we talk about the linguistic diversity of India, Kannada stands out as one of the most fascinating and historically significant languages. With a rich history spanning over a thousand years, Kannada has evolved to become a cornerstone of South Indian culture. This article delves into the nuances of 7 distinct Kannada dialects, their cultural significance, and how they have shaped the identity of the Kannada-speaking community.
Kannada, an official language of the state of Karnataka in India, is not just a medium of communication but a vibrant tapestry woven with centuries of tradition, art, and literature. Understanding its dialects is essential to appreciating its cultural depth.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive exploration of the 7 Kannada dialects, offering insights that cater to both linguistic enthusiasts and those curious about cultural heritage. By the end of this piece, you'll have a deeper appreciation for the linguistic richness that defines Kannada.
Read also:Alexandre Arnault The Visionary Entrepreneur Redefining Luxury
Table of Contents
- The History of Kannada
- Understanding the 7 Kannada Dialects
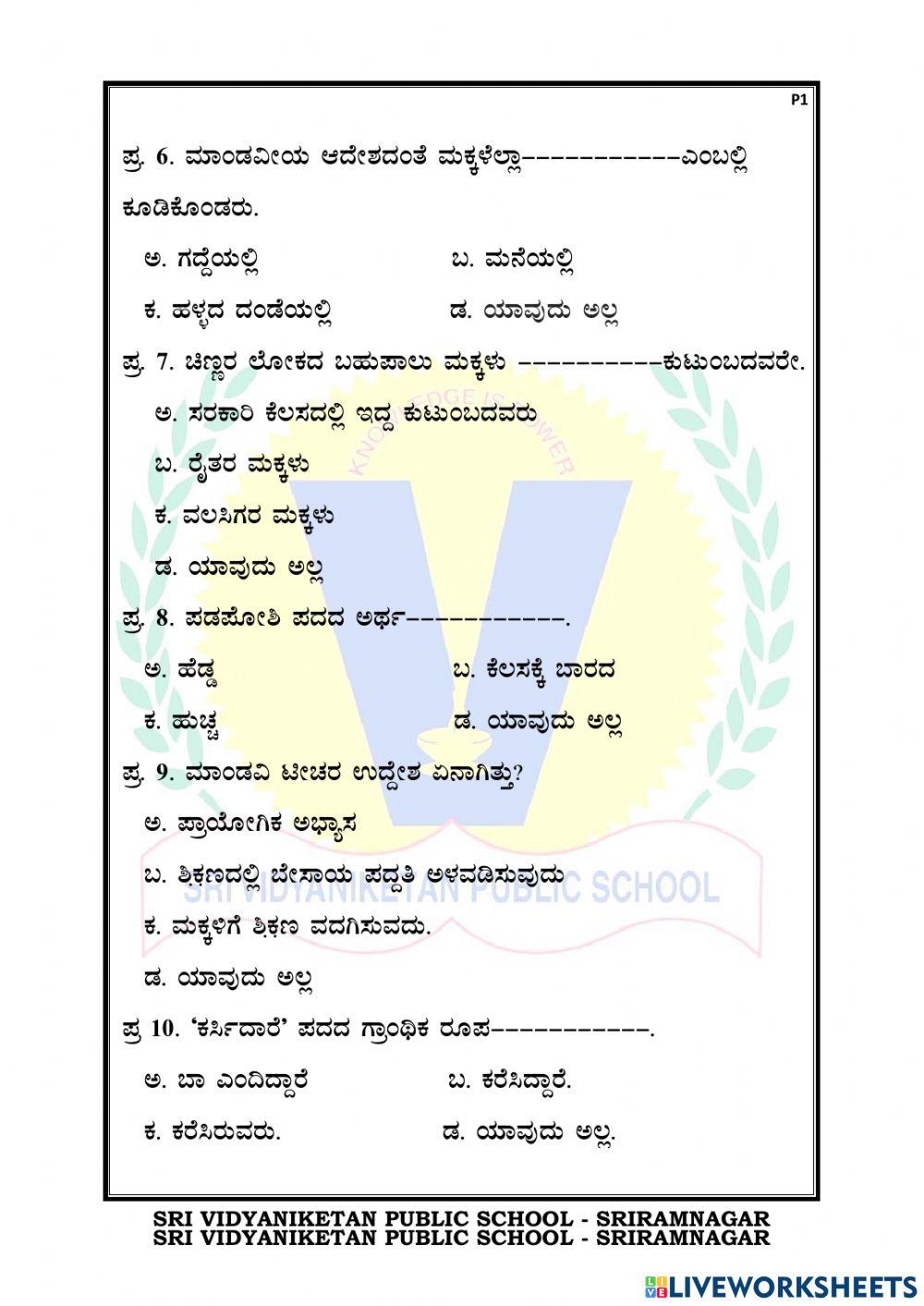
- Dialect 1: Old Kannada
- Dialect 2: Havyaka Kannada
- Dialect 3: Are Bhasha
- Dialect 4: City Kannada
- Dialect 5: North Karnataka Kannada
- Dialect 6: Coastal Kannada
- Dialect 7: Halakki Kannada
- Cultural Significance of Kannada Dialects
- Efforts to Preserve Kannada Dialects
- Conclusion
The History of Kannada
Kannada, one of India's classical languages, has a documented history dating back to the 5th century AD. The earliest known inscription in Kannada was found in the Halmidi inscription, believed to be from around 450 AD. Over the centuries, Kannada has undergone significant changes, giving rise to various dialects that reflect regional influences.
The evolution of Kannada can be broadly categorized into three stages: Old Kannada (5th to 10th century), Middle Kannada (10th to 15th century), and Modern Kannada (15th century onwards). Each stage contributed to the linguistic diversity seen today.
Scholars argue that the diversification of Kannada dialects was influenced by factors such as geography, socio-economic conditions, and interactions with neighboring cultures. This linguistic diversity is a testament to the adaptability and resilience of the Kannada-speaking community.
Understanding the 7 Kannada Dialects
While Kannada is a single language, its dialects vary significantly across regions. These dialects are not merely linguistic variations but reflect the cultural and social identities of the communities that speak them. Below, we explore the 7 Kannada dialects in detail:
Dialect 1: Old Kannada
Old Kannada is the earliest form of the language, primarily used in inscriptions and early literature. It reflects the classical roots of Kannada and is still studied by linguists and historians. Key characteristics include:
- Complex sentence structures
- Use of archaic vocabulary
- Prevalent in ancient inscriptions and manuscripts
Old Kannada serves as the foundation for all modern Kannada dialects.
Read also:Who Is Chase Stokes A Comprehensive Look Into The Rising Star
Dialect 2: Havyaka Kannada
Havyaka Kannada is predominantly spoken by the Havyaka Brahmin community in Karnataka. It is notable for its distinct pronunciation and vocabulary. Some unique features include:
- Distinctive vowel sounds
- Influence of Sanskrit and Tulu
- Rich literary tradition
Havyaka Kannada is an important marker of cultural identity for the Havyaka community.
Dialect 3: Are Bhasha
Are Bhasha, spoken in the coastal regions of Karnataka, is heavily influenced by Tulu and Konkani. It is characterized by:
- Simple sentence structures
- Unique phonetic variations
- Rich oral traditions
This dialect plays a crucial role in preserving the cultural heritage of the coastal communities.
Dialect 4: City Kannada
City Kannada, also known as Urban Kannada, is a modern dialect spoken in urban centers like Bangalore. It incorporates loanwords from English and other languages. Key features include:
- Code-switching between Kannada and English
- Adaptation to global communication trends
- Popular in media and entertainment
City Kannada reflects the dynamic nature of urban Kannada-speaking communities.
Dialect 5: North Karnataka Kannada
North Karnataka Kannada is spoken in regions like Dharwad, Gadag, and Bijapur. It is influenced by Marathi and Urdu. Notable characteristics are:
- Distinctive intonation patterns
- Influence of neighboring languages
- Rich folklore traditions
This dialect is a testament to the cultural exchanges between Karnataka and neighboring states.
Dialect 6: Coastal Kannada
Coastal Kannada, spoken in regions like Mangalore and Udupi, is heavily influenced by Tulu and Konkani. It is characterized by:
- Distinct phonetic features
- Influence of maritime culture
- Rich oral storytelling traditions
Coastal Kannada is an integral part of the cultural identity of the coastal communities.
Dialect 7: Halakki Kannada
Halakki Kannada is spoken by the Halakki Vokkaliga community, primarily in the Uttara Kannada district. It is notable for:
- Unique vocabulary and grammar
- Preservation of traditional customs
- Rich agricultural heritage
Halakki Kannada is a vital link to the agrarian past of Karnataka.
Cultural Significance of Kannada Dialects
Each Kannada dialect carries cultural significance, reflecting the traditions, customs, and lifestyles of its speakers. The diversity of Kannada dialects is a celebration of the state's multicultural heritage. For instance:
- Havyaka Kannada preserves the literary traditions of the Brahmin community.
- Coastal Kannada reflects the maritime history of the region.
- Halakki Kannada highlights the agricultural roots of the community.
Understanding these dialects provides a deeper appreciation of Karnataka's cultural tapestry.
Efforts to Preserve Kannada Dialects
Preserving Kannada dialects is crucial to maintaining the state's cultural diversity. Various initiatives have been undertaken to document and promote these dialects:
- Language documentation projects by universities and research institutions
- Community-led efforts to preserve oral traditions
- Government programs to promote regional languages
These efforts ensure that the linguistic heritage of Karnataka is passed down to future generations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the 7 Kannada dialects represent the rich linguistic and cultural diversity of Karnataka. From Old Kannada to Halakki Kannada, each dialect tells a unique story of the region's history and evolution. By understanding and preserving these dialects, we contribute to the preservation of Karnataka's cultural identity.
We invite you to explore more about Kannada and its dialects. Share your thoughts in the comments below, and don't forget to check out our other articles on Indian languages and culture. Together, let's celebrate the beauty of linguistic diversity!
Data Source: UNESCO | Karnataka Government | Linguistic Society of America